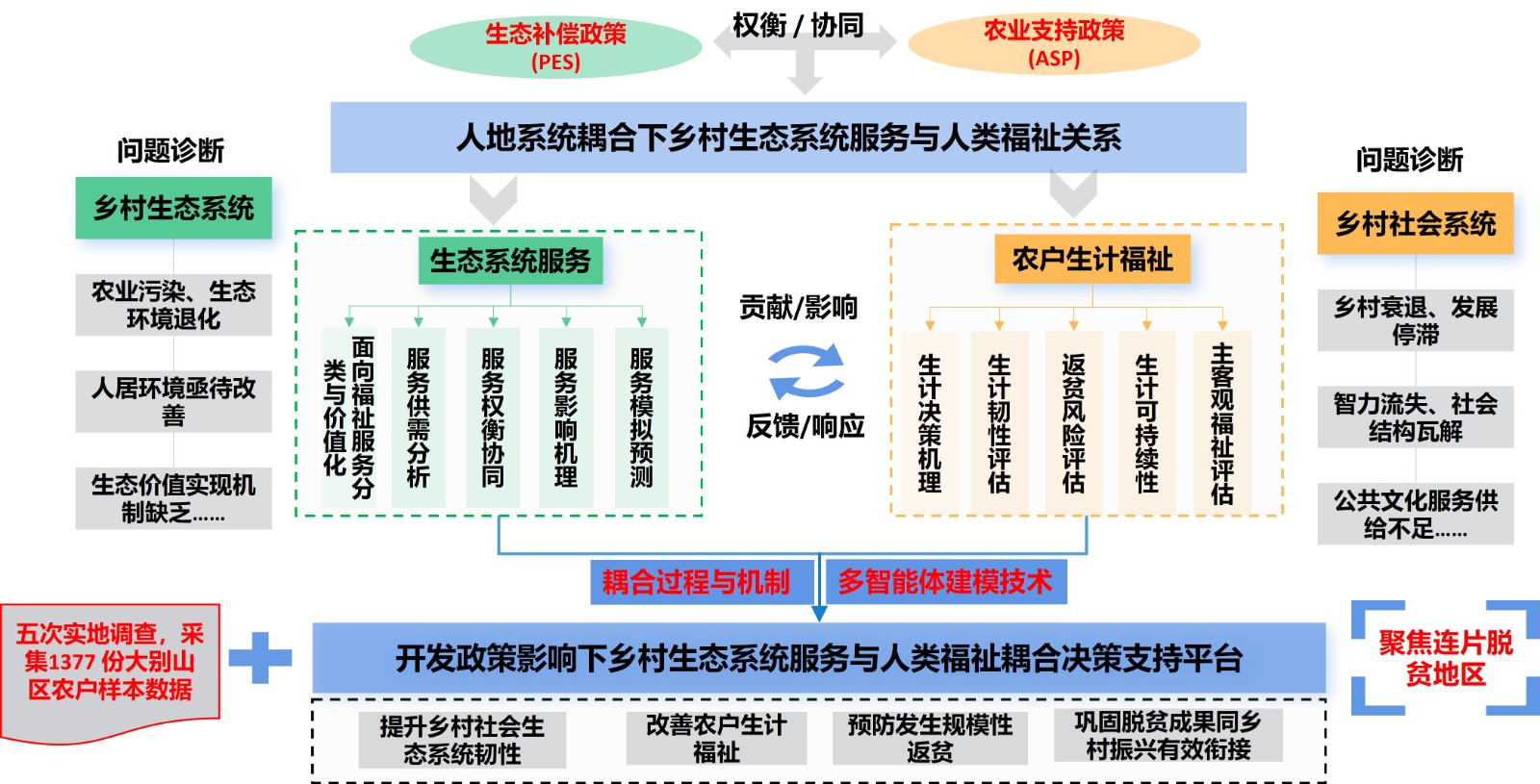
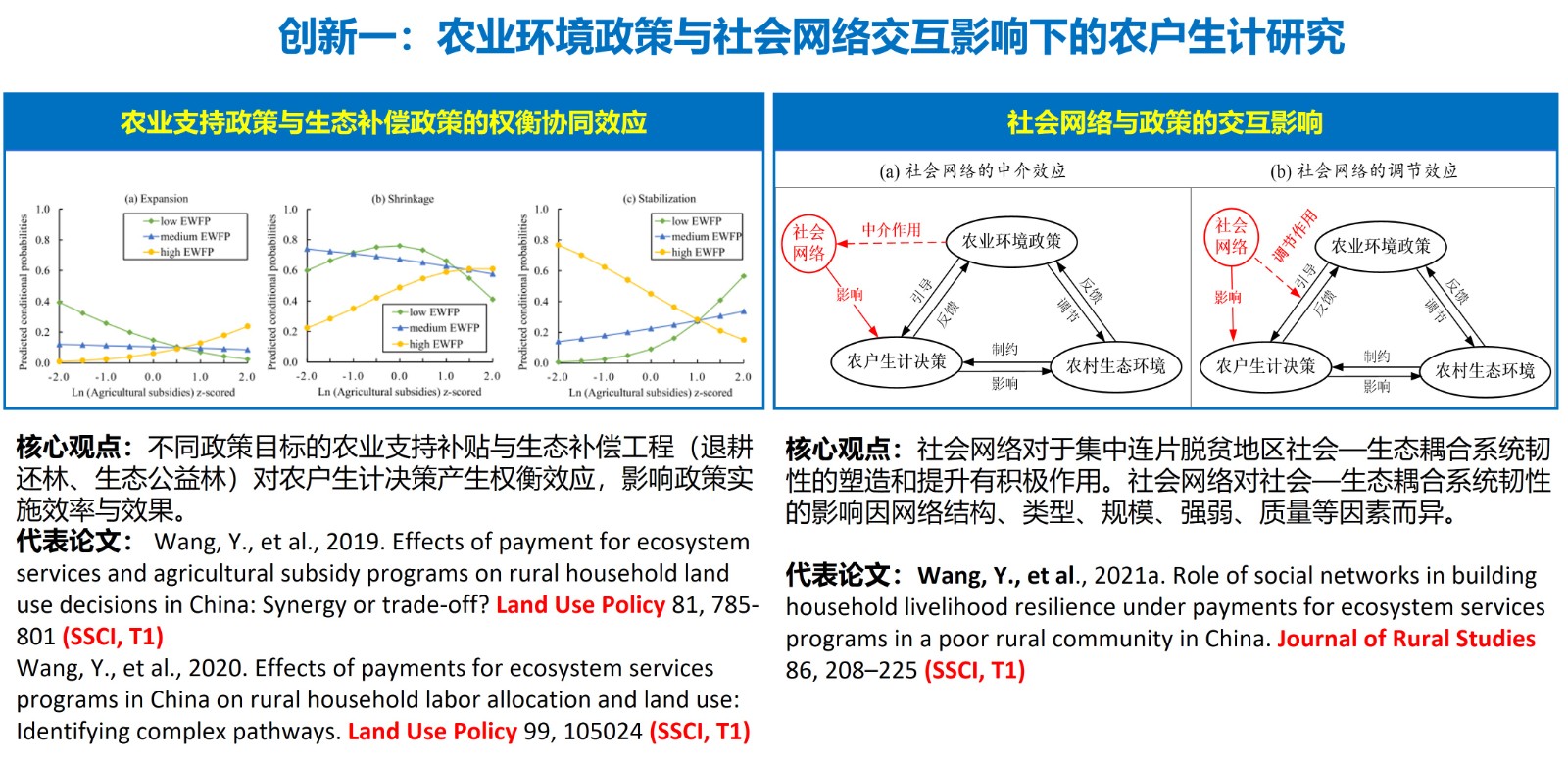
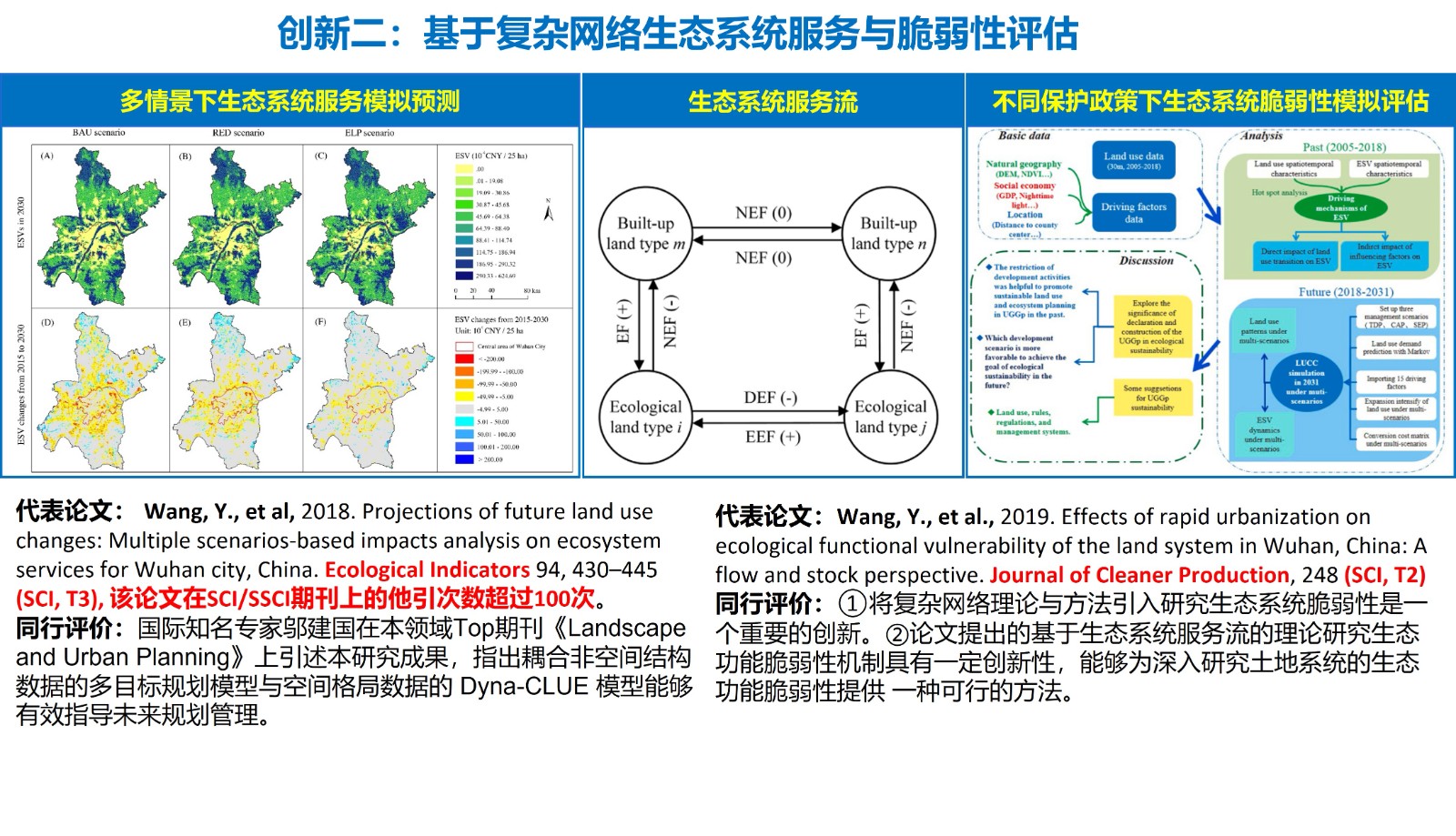
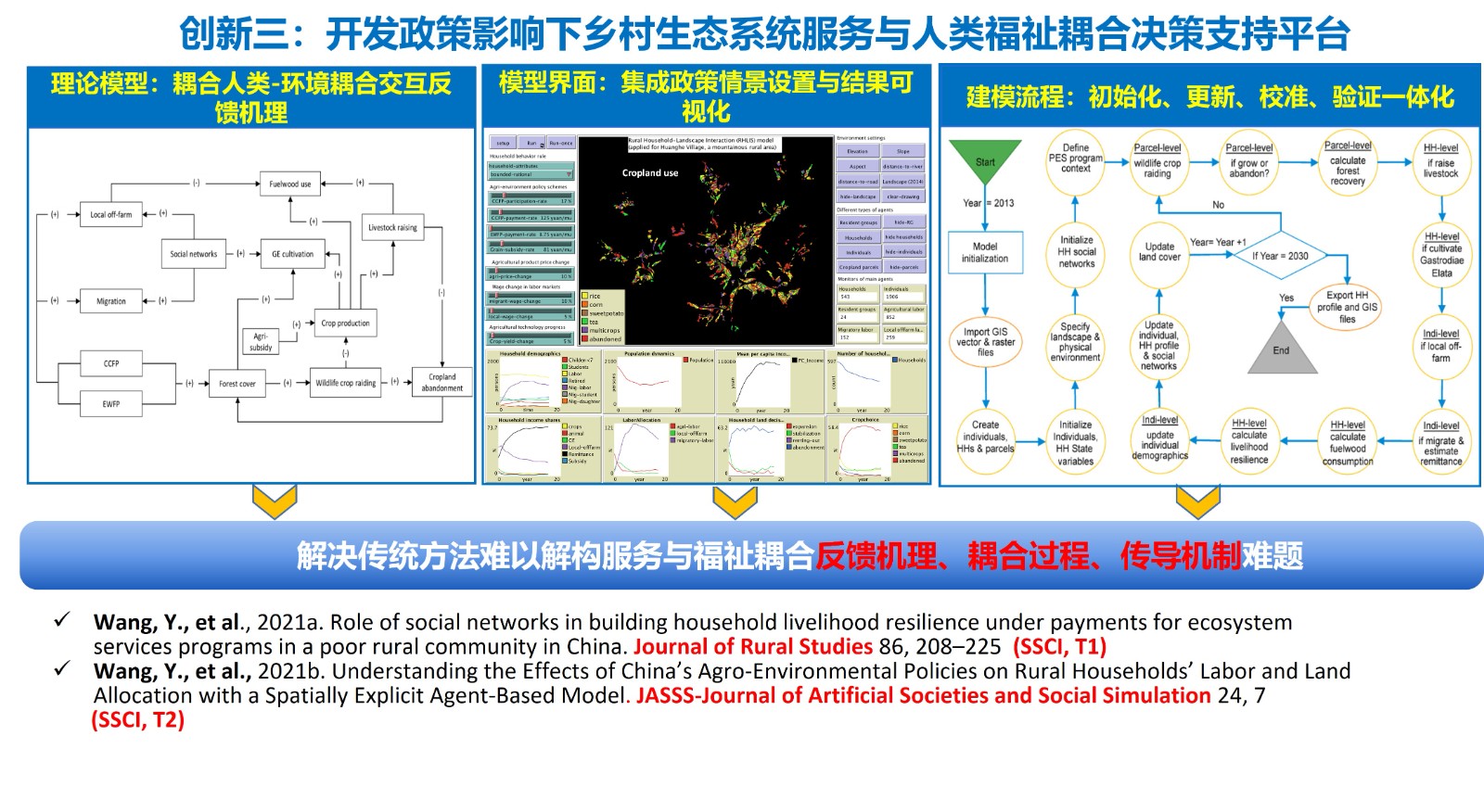
- 多维风险交互下的生态系统服务与农户生计福祉耦合机理及风险管控,2024-01-01,在研
- 社会网络和农业环境政策交互影响下农户生计响应、生态环境效应与政策优化路径,2020-01-01,结题
- 生态补偿政策、地理空间因素与社会网络影响下的农户可持续生计研究,2023-08-01,在研
- 生态补偿政策引导下连片特困地区农户生计转型:特征、机理与调控,2020-03-01,结题
- 社会网络嵌入下的社会-生态耦合系统韧性提升路径——以湖北大别山集中连片特困地区为例,2020-12-01,结题,湖北省教育厅哲学社会科学研究项目
- 暂无内容
- 暂无内容
- Wang, Y*., Sun, J., Liu, C., Liu, L., 2024. Exploring the nexus between perceived ecosystem services and well-being of rural residents in a mountainous area, China. Applied Geography 164.
- Zhang, Q., Gong, J., Wang, Y*., 2024. How resilience capacity and multiple shocks affect rural households’ subjective well-being: A comparative study of the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins in China. Land Use Policy 142.
- Cui, H., Wang, Y*., Zheng, L., 2024. Livelihood sustainability of rural households in response to external shocks, internal stressors and geographical disadvantages: empirical evidence from rural China. Environment, Development and Sustainability.
- Wu, D., Zheng, L., Wang, Y*., Gong, J*., Li, J.F, Chen, Q., 2024. Characteristics of urban expansion in megacities and its impact on water-related ecosystem services: A comparative study of Chengdu and Wuhan, China. Ecological Indicators 158.
- Yang, B., Wang, Y*., Yang, H., Chen, F., 2024. How does regional economic integration affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research.