个人简介
窦杰,籍贯江苏徐州,东京大学博士,日本学术振兴会(JSPS)研究员、博士生导师、博士后合作导师、教授,地灾大数据与智慧防控中心主任,入选国家人社部高层次人才、湖北省高层次人才计划、武汉市英才计划 、中国地质大学(武汉)百人计划、地大学者学科骨干人才、创新群体核心骨干。现任国际地质灾害与减灾协会(ICGdR)理事、地质灾害智慧防控委员会(TC12)主席,中国岩石力学与工程学会AI实用化专委会常务委员等。主持国家及省部级项目10余项,2025年获中国卫星导航定位协会科技进步二等奖(R1)、自然资源部科学技术奖科技进步二等奖(R2)等3项,获日本第17届地震工程大会- Early Career Award、第 18 届留日中国人 优秀研究.创新成果表彰奖、连续3年入选全球前2%顶尖科学家榜单与中国爱思维尔高被引学者。担任国家自然基金、新西兰皇家学会、湖北省科技厅、广东省科技厅、江西省科技厅、教育部学位与研究生教育发展中心通讯评议专家。
先后任东京大学空间情报中心博士后,日本国家国立研究开发法人土木研究所研究员,日本学术振兴会研究员。从事地质灾害AI大数据智慧管控及机理演化研究,成功研发了地灾智能风险早期识别与气象地质灾害数字孪生预报软件平台。作为项目负责人(PI)主持并领导了10余项国家或省部级科研项目,主要是受日本国土交通(MLIT)部和日本文部省的资助,还负责土木研究所火山小组雷达的研究工作(由日本宇航天局签署的雷达影像在防灾中的应用)。迄今已发国际刊物、书章和会议130余篇,其中SCI 106篇,第一作者及通讯68篇,发表在 Earth-Science Reviews, Water Research, Landslides, Journal of Hydrology, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,Science of The Total Environment, Remote sensing of Environment,Environmental Modelling & Software 等多个国际学术刊物上,两篇文章分别入选2019年百篇顶级自然科学报告和SCI-TAO杂志最多引用奖,13篇ESI 1%高被引,2篇ESI 0.1%热点论文,Google scholar引用10200余次,H指数44,担任国际SCI期刊Frontiers in Earth Science副主编,担任Geocarto International , Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, Journal Mountain of Science, The Global Environmental Engineers等7个国际期刊编委,担任Remote Sensing主题编辑和Frontiers in Earth Science前沿编辑,受邀为Engineering Geology, Landslides, Earth-Science Reviews 等40多个国际SCI期刊审稿,授权发明专利和软著30余 项,主编及参编标准3部,在日本地球行星科学会议、地球科学论坛上等大型会议被作为邀请嘉宾作报告。担任第五届世界 滑坡大会、第三-第五届巴东国际地质灾害学术论坛BIGS2021-2025的大会及第14届国际工程地质大会与环境(IAEG)分会召集人。
个人主页
Google Scholar 主页、 Research Gate 主页、中国地大-国家站主页、 中国地大-未来技术学院 、地质灾害智慧管控课题组 AI-Geohazards 微信公众号 
研究领域与科研方向
主要从事地质灾害演化机理与AI智慧风险防控,数值模拟和遥感与GIS在降雨-水库-地震-人工诱发的地质灾害相关的预测预报研究工作。具体包括以下四个科研方向:
1)基于深度学习识别多源海量遥感影像数据(卫星,航片,雷达SAR, 无人机UAV,激光雷达-LiDAR等)地质灾害早期识别与灾变演化机理;
2)地质灾害智能风险评价与“天-空-地-深”多源、多尺度感知监测体系
3)基于灾害单体或小尺度灾区域结合室内模型实验与物理演化过程数值模拟,探明灾害孕灾-致灾-成灾机制;
4)“数据-物理-知识”过程驱动的数字孪生垂直大模型地质灾害预测预报,实现地灾快速响与智能化应急预警。
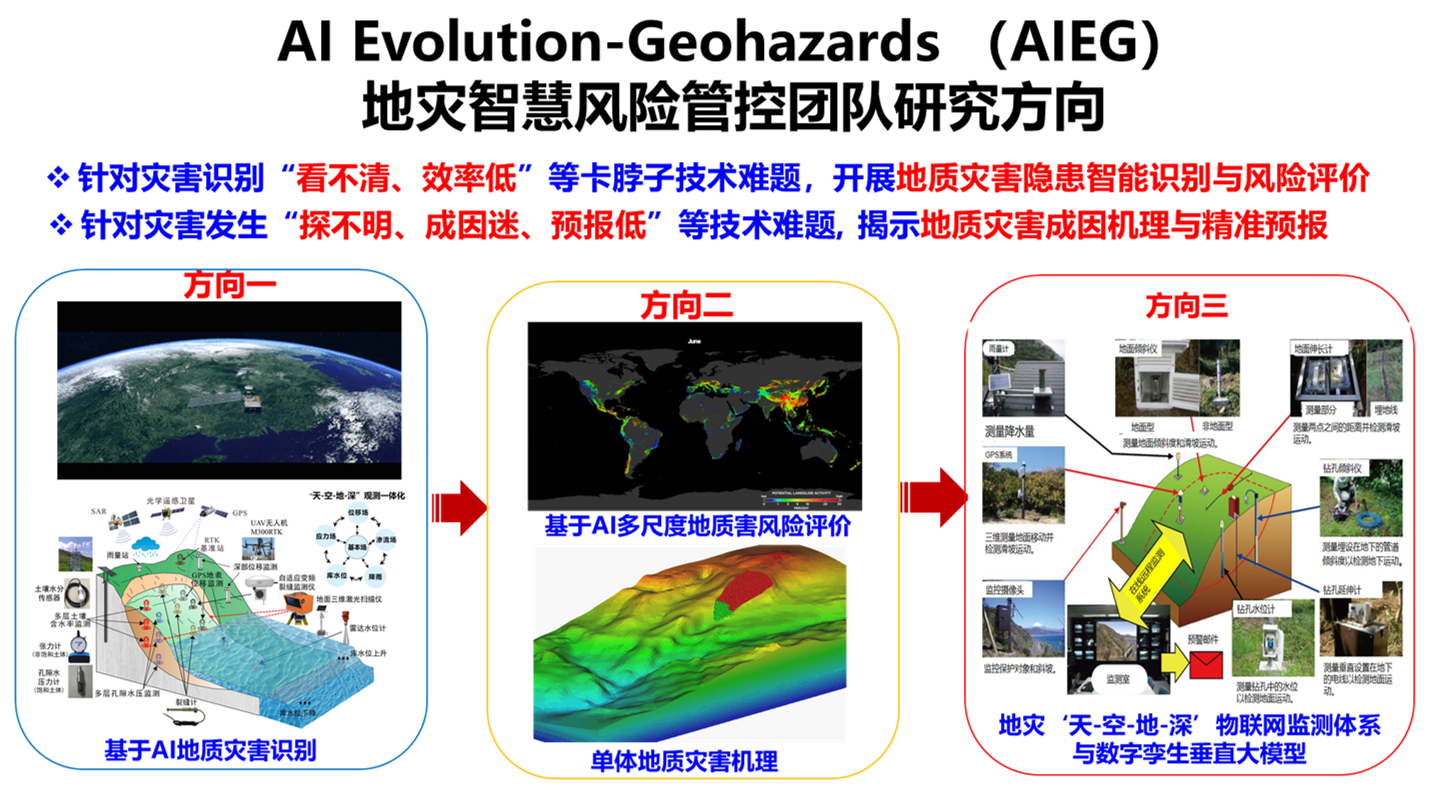
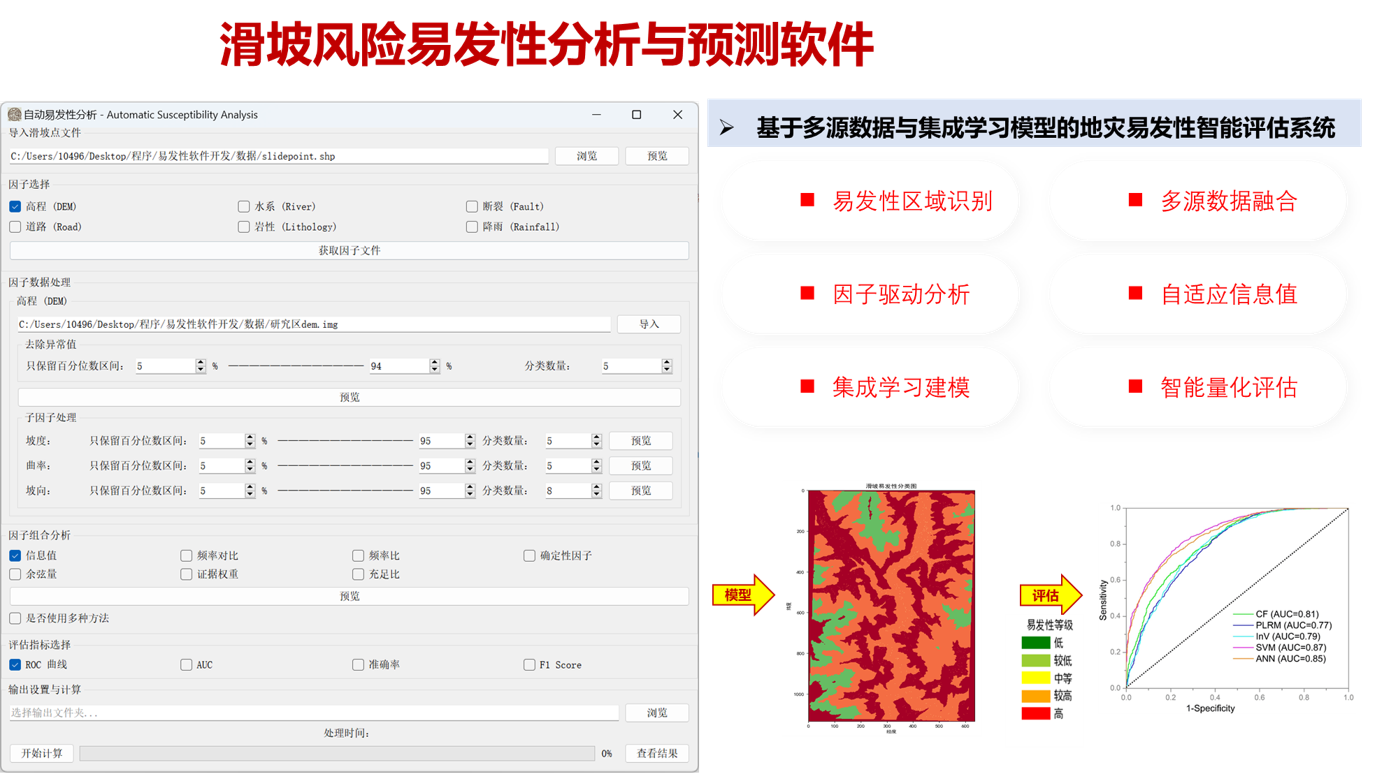
课题组开发的多模态识别软件、风险评价软件、及气象地质灾害数字挛生预报平台



招生与培养
招生方向:地质资源与工程,3S技术与地质灾害,AI大数据-计算机及地形地貌相关的专业。热烈欢迎具有深厚数学功底、计算机编程能力、力学以及相关专业背景的申请者。
在海外生活学习工作近十年中,与国际上相关地质灾害研究课题组建立了良好的合作关系,共同研究并发表科研论文。长期招收具有良好的数学计算机、数值模拟、3S技术、水文地形地貌、地质灾害基础知识的勤奋好学的硕士、博士研究生和博士后。我们热烈欢迎具有科学研究工作热情和抱负的申请者加入我们的团队。
加入我们,您将有机会成为国家野外观测研究站和教育部985优势地质灾害平台的一员,并加入AI Geohazards-地质灾害智能管控地质工程院士大团队,以地质资源与地质工程A+优势学科为主干,通过有组织的科研聚集科学问题,通过国家基金重大项目、重点研发、重点基金及重大水利水电工程项目, 突破地质灾害边界,融合跨领域、跨平台、跨学科的交叉,来解码地质灾害难题,共同探索地质灾害智能减灾防灾的未来,让我们携手努力,为人类的宜居地球而奋斗!
常年招生1-3个博士后,1-2博士生,2-4硕士!也欢迎优秀本科生加入课题组积极参与科研活动,同时也积极欢迎副教授或教授的加入,帮其推荐申请校内外各种人才计划。
欢迎咨询邮箱:doujie@cug.edu.cn、douj888@163.com
团队
AI-Geohazards-地质灾害智慧管控团队,与日本东京大学、北海道大学、日本国土交通部技術政策综合研究所和土木研究所、美国East Carolina University、University of South-Eastern Norway等单位保持长期的合作关系,面向国际科学前沿和国家重大工程的科学问题,立足于三峡于库区,开展地质灾害智能减灾防灾的研究工作。
目前团队已培养和在读硕士、博士及博士后共50余人,所有硕博研究生均顺利正常毕业并在大型央企、国企及相关事业单位就业,从事地质灾害监测、智慧防控等专业相关工作。
学生指导情况
1.2021.11:2020硕士生罗万褀、2021届王锐、何雨健、马豪分别获得第三届巴东国际地质灾害学术论坛,BIGS2021 Poster二等奖、三等奖及 优秀奖,向子林并在国际大会BIGS2021做口头报告
2.2021.11: 2021届向子林博士生分别获得三峡中心、中国地质大学2021年科技论文报告会一等奖和二等奖,2020硕士生罗万褀获得三等奖。
3.2022.10: 2022届博士生张乐乐、2021届王锐获国家站2022年科技论文报告会二等奖;2021届向子林博士生、2021届硕士生汪恒分别获国家站2022年科技论文报告会三等奖。
4.指导向子林博士以第一作者发表中科院TOP一区1篇文章,硕士生罗万褀以第一作者发表中科院二区1篇(高被引ESI1%),硕士生郭衍昊和何雨健分别以第一作者发表发表四区各一篇,2022届硕士董傲男以第一作者发表T2一篇。
5.2023.5:张乐乐与王锐分别获得中国地质大学第33届学生科技论文报告会三等奖。
6.2023.9:2021届王锐,2022届董傲男、Hamza Daud获得国际会议BIGS2023学术海报三等奖。
7.2023.9:2021届向子林博士在14届国际环境工程大会IAEG做口头学术报告,2022届董傲男和邢珂分别作国际学术海报。
8.2023.11:2022届董傲男和邢珂分别获得2023年国家站科报会一等奖和三等奖,同时他们俩也获第34届科技报告会一等奖和三等奖。获优秀指导老师称号。
9.2024:2022届董傲男分别第一作者发表一区T1&T2各一篇获得国家最高奖学金,博士生张乐乐发表T1一区文章,同时入选首批中国科协青年人才托举工程专项计划,向子林博生(国家公派CSC资助)成功从意大利进行公派交换留学归来(发表2T1&1T2),何雨健(院优秀毕业生称号)。
10.2025.10:博士生张乐乐-获得国家奖学金。
11.2025.11:国际工程地质与环境协会第15届亚洲区域会议(The 15th Asian Regional Conference of IAEG, ARC-15)大会上(尼泊尔首都加德满都) 董傲男博士生荣获大会颁发的“最佳海报展示奖”(共2人),邢珂博士生获得YEG最佳口头报告奖(共3人)。指导Hamza Daud留学生以第一作发表两篇T1-SCI文章。
毕业生:
硕士:
2023年:1. 罗万褀 (西北大学转博);2.郭衍昊(湖北省-地调局水环中心)
2024年:1.何雨健 (中国电建集团成都勘测设计研究院有限公司, 优秀毕业生); 2. 尧单(中国长江三峡集团);3.汪恒(中国能源建设集团甘肃兰州省电力设计院有限公司);4. 王锐 (南京苏交科集团股份有限公司);5.马豪(云南昆明地矿局第一水文队)
2025年:1.梁文欣(中广核, 校优秀毕业生);2.杨玉川(中国地质调查局军民融合地质调查中心, 发表中科院TOP 一区文章);3.田笑(中建八局一公司);4.邢珂与董傲男,课题组博士深造;5.向子林博士 (省防灾中心、华能水电);6.汤红(本科生, 武大硕士深造)
教育背景
2012-2015 东京大学 新领域创成科学研究科 博士学位
2006-2009 中国科学院 地球科学院 硕士学位
2002-2006 青岛农业大学 资环学院 学士学位
工作履历
2021.12-至今,中国地质大学(武汉) 地质灾害国家野外科学观测研究站/教育部长江三峡库区地质灾害研究中心
2020-2021 中国地质大学(武汉) 教育部长江三峡库区地质灾害研究中心
2019-2020 日本学术振兴会 研究员
2016-2019 日本国立研究开发法人 土木研究所 研究员
2015-2016 东京大学空间情报中心 博士后
2011-2012 日本アカデミック エクスプレス株式会社 助理工程师
2010-2011 中国赴日本国留学生东北师范大学预备学校日语培训
2009-2010 广州奥格公司项目经理
社会兼职
学术兼职
学会任职
ICGdR国际地质灾害减灾防灾终身会员、日本滑坡学会会员、日本砂防学会会员、日本地球行星科学連合会员和国际工程地质与环境协会(IAEG)会员、美国地球物理学会(AGU)会员、欧洲地球科学学会(EGU)会员、中国地震学会地震灾害链专业委员会委员,中国地质协会终身会员
国内外期刊编委
Frontiers in Earth Science (IF=3.34) 副主编
Geoenvironmental Disasters,Geocarto International, Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk,Journal Mountain of Science, Journal of Geography and Geology 编委
地质科技通报、深地科学、地球科学 编委
Remote Sensing, Natural Hazards, Deep Underground Science and Engineering, Geoscience, Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, Frontiers in Earth Science, Sensors 专题主编
最佳审稿人:
Journal Mountain of Science, International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction(Top 10 Outstanding Reviewer, Elsevier, 2024),地质科技通报
国际期刊审稿
Earth-Science Reviews, Geomorphology, Engineering Geology, Geoscience Frontiers, Science of The Total Environment, CATENA, Nature scientific report, Natural hazards, Remote sensing, Journal of Mountain Science, Theoretical and Applied Climatology, Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, Arabian Journal of Geosciences, Geocarto International, Journal of African Earth Sciences, Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, International Journal of Digital Earth, Geoscience, ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, Mathematical and Computational Applications, Engineering with Computers, The Professional Geographer, Advances in Space Research, Geosciences, Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction等40多个SCI审稿人。
主持项目及核心骨干( 纵向):
1. 动水驱动型滑坡启滑机制与判据课题(第二负责人)-子课题负责人,国家自然科学基金重大项目(2021-2025) (42090054)
2. 机理-数据双驱动下库岸滑坡演进过程与启滑判据研究 ,国家自然科学基金委面上项目(2025-2029)(42477170)
3. 人工智能地质灾害减灾防灾,中央高校高层次人才科研经费(2021-2026)
4. 基于深度学习的山区流域多源地质灾害链预测研究,四川大学水力学与山区河流开发保护国家重点实验室基金资助项目(2020-2022)(SKHL1903)
5. Cognitive modeling for dynamic long-term landslide assessment associated with extreme events in emergency preparedness and disaster management,日本学术振兴会(2019-2020) (1074088)
6. 基于地质地形因素对地表崩塌的发生与评价研究日本国土交通部 (2015-2018)
7. Coupling ensemble machine learning with physical parameters framework for landslide evaluation四川大学水力学与山区河流开发保护国家重点实验室基金资助项目(2021-2022)(SKHL2003)
8. 基于长时序监测数据的三峡库区地质灾害时空演化机制与风险动态预警,湖北省科技厅联合基金重点项目( 2025-2028)
9. 水库运行条件下重大滑坡风险动态预测研究,三峡集团实验室开放基金,水资源高效利用与工程安全国家工程研究中心 ( 2024-2026)
10. 国家高层次人才计划 (2022-2025)(20233040018)
11. 武汉英才优秀青年人才项目 (2023-2024)( 20233050043)
12. 重大滑坡地质灾害演化机理与预测预报 创新群体 (2022-2024)(No.2022CFA002)
13. 长时间序列下的多场耦合库岸滑坡智能监测预警 三峡库区地质灾害教育部实验室重点开放基金(2024-2025)(2023KDZ02)
14. 知识图谱驱动的地质灾害易发性动态评价研究,实验室开放基金,资源与生态环境地质湖北省重点实验室 (2025-2025)
15. 深层滑坡监测观测技术研究,日本国土交通部萌芽 (2016-2018)
16. 基于地质灾害移动的损伤预测监视技术的开发研究,日本国土交通部重点(2015-2019)
17. 广东省地质灾害数据建设 广东省科技厅(2006-2009)
18. 水库运行条件下重大滑坡物理启滑机制与风险动态预测研究,湖北省科技厅联合基金重点项目( 2024-2027)(2025AFD435)
主持项目及核心骨干( 横向):
1. 库岸滑坡地质灾害体智能识别技术 中国电建集团华东勘测设计研究院(2022-2024)(KY2021-ZD-03)
2. 湖北省襄阳市2024年度地质灾害监测台站建设项目选点及设计 (2023-2024)
3. 云南2024年度1:1万地质灾害调查及数据库建设 (2023-2024)
4. 广东省鹤山市蟠龙矿区建筑用花岗岩矿边坡稳定性分析研究,横向一般项目 (2024-2024)
5. 广东省佛冈县石角镇诚迳矿区建筑用花岗岩矿采场边坡稳定性研究,横向一般项目(2025-2025)
6.江西地质灾害气象地质风险预警模型系统开发,横向一般项目(2024-2025)
7.云南省地质灾害精准化调查(红河县)技术服务,横向一般项目 (2024-2026)
8. 动水驱动下重大水库滑坡智能识别, 中国长江电力股份有限公司,横向项目(2024-2026)
9. 库区高位远程地质灾害发育特征及高速远程滑坡、冰湖识别及溃决风险评估,中国电建集团成都勘测设计研究院有限公司 (2023-2025)
近年主要论文 (*代表通讯,#共同一作)
1. Dou, Jie*, Yunus, A.P., Tien Bui, D., Merghadi, A., Sahana, M., Zhu, Z., Chen, C.-W., Khosravi, K., Yang, Y., Pham, B.T., 2020. Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning. Science of the Total Environment https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137320 (SCI=10.75 -ESI 1% 高被引)
2. Abdelaziz Merghadi1#, Ali P. Yunus2#, Dou Jie#*, Jim Whiteley, Binh Thai Pham. Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: a comparative overview of algorithm performance, Earth-Science Reviews, 207 (August): 103225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103225. (SCI=12.41 ESI 1% 高被引及热点论文)
3. Dou, Jie*, Yunus, A.P., Tien Bui, D., Merghadi, A., Sahana, M., Zhu, Z., Chen, C.-W., Khosravi, K., Yang, Y., Pham, B.T., 2019. Assessment of advanced random forest and decision tree algorithms for modeling rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan. Science of the Total Environment 662, 332–346. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.221 (SCI=10.75 -ESI 1% 高被引)
4. Dou Jie*, Yunus, A.P., Bui, D.T., Merghadi, A., Sahana, M., Zhu, Z., Chen, C.-W., Han, Z., Pham, B.T., 2019. Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging, boosting, and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed, Japan. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01286-5 (SCI=6.578-ESI 0.1% 高被引及 热点论文)
5. Dou, Jie*, et.al. Evaluating GIS-Based Multiple Statistical Models and Data Mining for Earthquake and Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility Using the LiDAR DEM. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, doi:10.3390/rs11060638. (SCI=5.349 -ESI 1% 高被引)
6. Dou Jie*, Chang K-T*, Chen S, et al. 2015. Automatic Case-Based Reasoning Approach for Landslide Detection: Integration of Object-Oriented Image Analysis and a Genetic Algorithm. Remote Sensing 7:4318–4342. doi: 10.3390/rs70404318 (SCI=5.349)
7. Dou Jie*, Yunus, A.P., Xu, Y., Zhu, Z., Chen, C.-W., Sahana, M., Khosravi, K., Yang, Y., Pham, B.T., 2019. Torrential rainfall-triggered shallow landslide characteristics and susceptibility assessment using ensemble data-driven models in the Dongjiang Reservoir Watershed, China. Natural Hazards 97, 579–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03659-4 (SCI=2.427)
8. Chang, K.-T., Merghadi, A., Yunus, A.P., Pham, B.T., Dou Jie*. Evaluating scale effects of topographic variables in landslide susceptibility models using GIS-based machine learning techniques. Nature Scientific report vol. 9, no. 1, 2019, p. 12296, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-48773-2. (SCI=4.996, 自然 科学报道Selected as Top 100 rank, ESI 1% 高被引)
9. Dou, Jie*, Li, Xia, Yunus, Ali P., et al. (2015). An Integrated Artificial Neural Network Model for the Landslide Susceptibility Assessment of Osado Island, Japan. Natural Hazards, 1–28. doi:10.1007/s11069-015-1799-2. (SCI=3.158)
10. Dou Jie*, Tien Bui, Dieu, P. Yunus, Ali et al (2015). Optimization of Causative Factors for Landslide Susceptibility Evaluation using Remote Sensing and GIS data in parts of Niigata, Japan, Plos one, 10.1371/journal.pone.0133262 (SCI=3.53)
11. Dou Jie*, Li X, Yunnus Ali, et al. (2015). Automatic detection of sinkhole collapses at finer resolutions using a multi-component remote sensing approach, Natural hazards DOI: 10.1007/s11069-015-1756-0. (SCI=3.158)
12. Hai-bo Li#, Yue-ren Xu#, Jia-wen Zhou#, Xie-kang Wang#, Hiromitsu Yamagishi, Dou, Jie#*. Preliminary analyses of a catastrophic landslide occurred on July 23, 2020, in Guizhou Province, China. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01334-0 (SCI=6.578)
13. Han, Zheng, Bin Su, Yange Li, Dou Jie, Weidong Wang, and Lianheng Zhao. Modeling the Progressive Entrainment of Bed Sediment by Viscous Debris Flows Using the Three-Dimensional SC-HBP-SPH Method, Water Research, 182,116031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116031(SCI =9.130 )
14. Ali P.Yunus; Xuanmei Fan, Xiaolu Tang; Dou Jie, Qiang Xu, Runqiu Huang. Decadal vegetation succession from MODIS reveals the spatiotemporal evolution of post-seismic landsliding after the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020 (SCI=13.850)
15. Yunus AP, Dou, Jie*, Song X, Avtar R (2019) Improved Bathymetric Mapping of Coastal and Lake Environments Using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 Images. Sensors 19:2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122788 (SCI=3.23)
16. Dou Jie, Paudel U, Oguchi T, et al (2015). Differentiation of shallow and deep-seated landslides using support vector machines: a case study of the Chuetsu area, Japan (SCI) Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2014.12.02.07(EOSI) (SCI=1.1)
17. Dou Jie, Qian, J., Chen, S., & Zhen, X. (2010). Object-based and case-based reasoning method for ground collapses detection. Journal of Image and Graphics, 1 5(6), 900–910. (In Chinese)
18. LV, Y., Le, Q., Bui, H.-B., Bui, X., Nguyen, H., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Dou Jie*, Song, X., 2020. A Comparative Study of Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting the Content of Ilmenite in Titanium Placer. Appl. Sci. 10, 635. (SCI=2.217)
19. Zhu, Z., Wang, H., Peng, D., Dou, Jie*, 2019. Modeling the hindered settling velocity of a falling particle in a particle-fluid mixture by the Tsallis entropy theory. Entropy (SCI=2.305)
20. Shariati, M., Mafipour, M.S., Mehrabi, P., Bahadori, A., Zandi, Y., Salih, M.N.A., Nguyen, H., Dou Jie*, Song, X., Poi-Ngian, S. Application of a Hybrid Artificial Neural Network-Particle Swarm Optimization (ANN-PSO) Model in Behavior Prediction of Channel Shear Connectors Embedded in Normal and High-Strength Concrete. Appl. Sci. 9, 5534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245534 (SCI=2.217)
21. Khosravi, K., Shahabi, H., Pham, B.T.*, Adamowski, J., Shirzadi, A., Pradhan, B., Dou, Jie*, Ly, H.-B., Gróf, G., Ho, H.L., Hong, H.*, Chapi, K., Prakash, I.A Comparative Assessment of Flood Susceptibility Modeling Using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Analysis and Machine Learning Methods, 2019-Journal of Hydrology- (SCI=4.405 -ESI 1% 高被引)
22. Shariati, M.; Mafipour, M.S.; Mehrabi, P.; Bahadori, A., Zandi, Y.; Salih, M.N.A.; Nguyen, H*., Dou, Jie*; Song, X.; Poi-Ngian, S. Application of a Hybrid Artificial Neural Network-Particle Swarm Optimization (ANN-PSO) Model in Behavior Prediction of Channel Shear Connectors Embedded in Normal and High-Strength Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5534. ( SCI=2.217)
23. Dou Jie*. et al (2018). A Comparative Study of the Binary Logistic Regression (BLR) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Models for GIS-Based Spatial Predicting Landslides at a Regional Scale. Landslide Dynamics: ISDR-ICL Landslide Interactive Teaching Tools: Volume 1: Fundamentals, Mapping and Monitoring (eds. Sassa, K. et al.) 139–151 (Springer International Publishing, 2018). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-57774-6_10
24. Zhu, Z. & Dou Jie* (2018). Current status of reclaimed water in China: An overview. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination jwrd2018070. doi:10.2166/wrd.2018.070 (SCI=1.538)
25. Daniela Castro Camilo, Luigi Lombardoa, Martin Maib, Dou Jie, Raphaël Huser, 2017. Handling high predictor dimensionality in slope-unit-based landslide susceptibility models through LASSO-penalized Generalized Linear Model, 97:145-156. Environmental Modelling & Software. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.08.003 (SCI=4.807)
26. 窦杰, et al.2010. 基于对象的遥感案例推理方法检测岩溶地面塌陷. 中国图象图形学报 15.06(2010):900-909.
2023年
27. 窦杰, et al. 2023. 机器学习在滑坡智能防灾减灾中的应用与发展趋势. 地球科学 (三高论文, 高被引、高下载、高PCSI,百篇优秀论文)
28. Luo, W., Dou Jie*, Fu, Y., Wang, X., He, Y., Ma, H., Wang, R., & Xing, K. (2022). A Novel Hybrid LMD – ETS – TCN Approach for Predicting Landslide Displacement Based on GPS Time Series Analysis. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010229 (SCI=5.349, 高被引 ESI1%)
29. Xiang Z, Dou Jie*, Yunus AP, et al (2023) Vegetation-landslide nexus and topographic changes post the 2004 Mw 6.6 Chuetsu earthquake. CATENA 223:106946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2023.106946 (SCI=6.367 )
30. 郭衍昊 ,窦杰 *, et al. 2023. 机基于优化负样本采样策略的梯度提升决策树随机森林与随机森林梯度提升决策树模型的汶川同震滑坡易发性评价. 地质科技通报
31. 何雨健 ,窦杰 *, et al. 2023. 国内外免像控无人机航测软件在数字滑坡中的应用效果对比-以三峡库区黄土坡滑坡为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报
32. Ni W, Zhao L, Zhang L, Dou Jie* (2023) Coupling Progressive Deep Learning with the AdaBoost Framework for Landslide Displacement Rate Prediction in the Baihetan Dam Reservoir, China. Remote Sens 15:2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092296(SCI=5.349)
33. Dong A, Dou Jie* , Fu Y, et al (2023) Unraveling the Evolution of Landslide Susceptibility: A Systematic Review of 30-Years of Strategic Themes and Trends. Geocarto Int 38:1–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2023.2256308
2024年
34. Zhang L, Zhang R, Dou Jie* , et al. Advancing reservoir landslide stability assessment via TS-InSAR and airborne LiDAR observations in the Daping landslide group, Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China[J]. Landslides, 2025, 22(1): 169-188. (地T1)
35. Dou Jie , Xiang Z, Wang X, et al. Post-seismic topographic shifts and delayed vegetation recovery in the epicentral area of the 2018 Mw 6.6 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi earthquake[J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 2024, 48(4): 595-614. (地T1)
36. Xiang Z, Dou Jie* , Zhang L, et al. Towards a Synergistic Progressive Ensemble Framework for Automatic Post-Earthquake Landslide Recognition and Susceptibility Assessment[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2025: 1-30. (地大T1)
37. Yang Y, Dou Jie* , Merghadi A, et al. Advanced Prediction of Landslide Deformation through Temporal Fusion Transformer and Multivariate Time Series Clustering of InSAR: Insights from the Badui Region, Eastern Tibet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024. (地大、中科院T1)
38. Dong A, Dou Jie* , Li C, et al. Accelerating cross-scene co-seismic landslide detection through progressive transfer learning and lightweight deep learning strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024.(地大、中科院T1)
39.Dou Jie, Xing, K., Lu, Z. et al. Comprehensive analysis of July 17, 2024, heavy rainfall-induced landslide at Zigui County in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Landslides 22, 957–965 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-024-02442-2(地大T1)
2025年
40. Dou Jie, Xing, K., Wang, L. et al. Air-Space-Ground Synergistic Observations for Rapid Post-Seismic Disaster Assessment of 2025 Ms6.8 Xigazê Earthquake, Xizang. J. Earth Sci. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-025-0160-2(中科院T1)
41. 窦杰,唐辉明*,董傲男,黎昊, 邢珂,强巴南加,向新建, 张乐乐,韩梦嘉,2025.融合多尺度特征与注意力机制的地震地表裂缝智能识别与特征分析——以2025年西藏定日Ms6.8地震为例. 地球科学https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2025.058
42. 张世殊, 李青春, 黎昊, 向新建, 董傲男, 窦杰*, 2025. 融合多源遥感数据和改进的Mask R-CNN深度学习模型的复杂高原地形区冰湖智能识别. 地球科学. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2025.041
43. 邢珂,黎昊,张乐乐,郁军建,彭一桂,彭博,向新建,窦杰*.2025年1月7 日西藏定日Ms 6.8地震地表破裂与震害特征分析[J/OL].安全与环境工程. https://doi.org/10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20250133
44. Z Xiang, Dou Jie*, Huiming Tang, A Dong, B Peng, K Xing, L Zhang, H Daud, Z Lu, 2025. Deep learning-augmented crack mapping and SPH-based dynamic simulation for landslide kinematic prediction.Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (地大,中科院TOP 一区 IF=10.2)
45.H Daud, Dou Jie*, NG Khan, B Xu, S Dong, A Dong, H Ma,2025. Tree-Based Machine Learning and Flow Simulation for Debris Flow Susceptibility, Runout Propagation, and Dynamics in the Higher Himalayas.Mathematical Geosciences (地大一区)
46.Hamza Daud , Dou Jie*, Javed Iqbal Tanolie, et.al, 2025. The Role of Multi-Resolution DEMs and Sampling Strategy Uncertainty in Deep Learning-Based Debris Flow Susceptibility Mapping Acta Geotechnica (地大,中科院TOP 一区)
47. 邢珂,窦杰*,陈能成,邹宗兴,尤运飞, 向子林张乐乐,2025, 基于光学-LiDAR协同遥感及三维精细建模的滑坡特征解译与稳定性评价,自然灾害学报, 119-132
48. Daud, Dou Jie*, etal. 2025, Tree-Based Machine Learning and Flow Simulation for Debris Flow Susceptibility, Runout Propagation, and Dynamics in the Higher Himalayas, Mathematical Geosciences (地大1区)
48. Zhang L, Dou Jie*, et al.2025, Spatiotemporal reconstruction and post-failure stability analysis of rainfall-induced landslides via multi-modal SAR-optical data fusion, CATENA(中科院一区)
49. Z Xiang, Dou Jie*, et al.2025, Towards a Synergistic Progressive Ensemble Framework for Automatic Post-Earthquake Landslide Recognition and Susceptibility Assessment, Mathematical Geosciences (地大1区)
国内外会议主旨及特邀报告(40多场)
1. Estimating scale effects of multiple DEMs for landslide geohazard map using GIS-based artificial intelligence models, AGU, 2019, SanFrancisco, USA
2. GeohazardstriggeredbydeadlyHokkaidoIburi-TobuEarthquake(September 6, 2018, Mw6.7), Hokkaido, Japan,12thARCof IAEG,2019, Jeju, SouthKorean
3. Estimation of Distribution of Tephra Fall Deposit Using the Interpolation Method Based on Multi-observation Data, Interpraevent,2018, Toyama, Japan
4. High predictor dimensionality in slope-unit-based landslide susceptibility models through LASSO-penalized Generalized Linear Model,2017, EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria
5. Ellipse-approximated isopach(EAI) approach for assessing ashfall deposit at the active Sakurajima volcano, Japan,2016, Cities Volcanoes, Puerto Varas, Chile
6. Spatial resolution effects of digital terrain models on landslide susceptibility analysis,2016, Prague, Czech Republic
7. Analysis of the landslides in Hiroshima caused by the typhoon based on bivariate statistical landslide susceptibility,2015, JpGU, Makuhari, Japan
8. Shallow and Deep-Seated Landslide Differentiation Using Support Vector Machines: A Case Study of the Chuetsu Area, Japan, 2014, ICEO&SI, Taiwan, Taiwan
9. GIS-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using a Certainty Factor Model and Its Validation in the Chuetsu Area, Central Japan, 2014, The Third World Landslide Forum, Beijing, China
10. Back propagation (BP) model optimized by genetic algorithms (GA) for predicting landslides, IGU 2013 - Kyoto regional conference, Japan
11. Using Back-Propagation networks to predict the landslides based on 2m Lidar DEM, 2013, JpGU, Makuahri, Japan
12. Application of Support Vector Machines to predict landslides based on Lidar DEM: the Chuetsu earthquake case study, Japan, 2013, ICEO&SI, Taiwan.
软件著作权
1.融合数值模拟与I-D阈值的气象地质灾害风险预测预报软件,2024. 窦杰,唐辉明,张淞城,李杰,周凡皓,黎昊
2.基于数据随机增强的ResUNet深度学习模型滑坡裂缝识别软件,2023. 窦杰,李长冬,赵留园 ,董傲男,张乐乐
3.多源大数据融合技术驱动的地质灾害动态监测系统,2024. 窦杰,李长东,张淞城,杜高峰,阮班晓,代小俊,李杰
4.基于注意力机制的SE-VGG16的同震滑坡易发性评价软件V1.0,2023. 窦杰,李长冬, 董傲男, 王锐, 邢珂,杨玉川
5.基于核密度估计和DBSCAN聚类方法的凌空结构面识别软件,2024.窦杰,唐辉明,陶志刚,姬建,尧单
6. 基于轻量级编解码语义分割网络的滑坡智能识别软件V1.0,2023. 窦杰, 赵留园 ,李长冬, 董傲男, 王锐, 张乐乐, 邢珂
7. 基于CEEMDAN-GBDT-LSTM的库岸滑坡动态预测软件,2024.窦杰,周凡皓,陶志刚,姬建,胡燮,张杰
8. 基于树结构的人工智能滑坡易发性评价软件V1.0,2024. 窦杰,龚松林,马豪,董傲男,张乐乐
9. 三峡库区地质灾害实时监测系统软件[简称:地灾监测系统] V1.0, 2021.9.25
10. 基于和声分解-支持向量回归的滑坡时间序列位移智能预测软件 V1.0,2023.5.9 窦杰,王锐,梁文欣
11.基于优化负样本采样策略的Resnet深度学习模型滑坡易发性评价软件V1.0,2023. 窦杰, 董傲男,王锐,张乐乐,邢珂
12.基于长短时记忆神经网络的滑坡长时序监测数据智能预测软件V1.0,2023. 王锐,窦杰,梁文欣,董傲男,周凡皓
13. 融合记忆神经网络与遗传算法优化SVR模型的库岸滑坡时间序列位移智能预测软件V1.0,2023. 梁文欣,王锐,窦杰,周凡皓
14.多智能体耦合深度学习的滑坡时间序列位移组合预测软件,2023. 王锐,窦杰,梁文欣,向子林,周凡皓
15. 基于多统计参数的二维节理粗糙度系数非线性预测软件,2023. 梁文欣,窦杰,董傲男
16. 基于智能算法的地质灾害裂缝识别与精确计量系统,2024. 窦杰,张淞城,翁茂芝,刘磊,程靖清,董傲男
发明专利
1 基于AdaBoost框架的深度学习滑坡位移预测方法, 2023 申请. 窦杰, 梁文欣, 董傲男, 王锐, 罗万祺
2 一种基于尺度无味变换法的边坡可靠性分析技术,2023申请. 窦杰,向子林
3 基于GBDT的二维节理粗糙度系数非线性确定性方法,2025. 窦杰,梁文欣,汤红
4 基于InSAR 滑坡易发性评价方法、装置、设备和介质,2024申请. 窦杰,张佳磊,董傲男,杜高峰
5 基于多路径特征融合的滑坡识别方法、设备及存储介质,2024 窦杰,董傲男,张淞城,黎昊,彭一桂
6 一种滑坡易发区识别方法、装置及存储介质,2024申请. 邢珂、窦杰、翁茂芝、刘磊、董傲男、梁文欣、杨玉川
获得荣誉
1. 国家高层次人才、2021年入选湖北省高层次人才计划、2020年中国地质大学百人计划、武汉市英才计划 (2022)、第18届留日中国人 优秀研究.创新成果表彰奖 (2022)、入选全球前2%顶尖科学家榜单(2022、2023、2024)、高被引学者(2023、2024)
2. 2018年获日本学术振兴会(JSPS)特别研究基金
3. 2021年获获得日本第17届地震工程大会- "Early Career Award"
4. 2011年获日本政府(文部科学省-MEXT)博士生奖学金
5. 2014年东京大学新领域创成科学研究科科学研究基金
6. 2019年,论文“Shallow and Deep-Seated Landslide Differentiation Using Support Vector Machines: A Case Study of the Chuetsu Area, Japan” published in TAO Journal has won the Most Cited Article Award in 2019。入选SCI杂志TAO最多引用奖
7. 2020年,论文“Evaluating scale effects of topographic variables in landslide susceptibility models using GIS-based machine learning techniques”。入选百篇自然科学报告-Top 100 Nature Scientific Reports paper
8. 2008年中科院学术报告一等奖
9.2024年优秀指导老师和本科生“优秀班主任”
10.2024年湖北省科技期刊百篇优秀论文-地球科学
11.荣获DF2024第七届国际泥石流会议最佳报告奖
12.2025年湖北省科技期刊百篇优秀论文-地质科通报
13.2025年中国卫星导航定位协会科技进步二等奖(R1)、自然资源部科学技术奖科技进步二等奖(R2)
14.继续入选中国高被引科学家和全球前2%顶尖科学家
曾获荣誉
[1] 人社部高层次人才(2022) 湖北省高层次人才(2021) 武汉市英才计划 (2022) 入选全球前2%顶尖科学家榜单与中国爱思维尔高被引学者(2022-2024) 中国地质大学(武汉)百人计划(2020) 日本学术振兴会(JSPS)特别研究员(2019) 第18届留日中国人 优秀研究.创新成果表彰奖 (2022) 日本第17届地震工程大会- "Early Career Award"(2021) 日本文部省博士研究生国家奖学金 (2011)
其他联系方式
邮编:
通讯/办公地址:
办公室电话:
移动电话:
邮箱:
团队成员
团队名称:AI Geohazards-地质灾害智能管控
团队介绍:常年招生1-2博士生,2-4硕士,1-3个博士后!
目前在读:
博士二名
硕士七名
一名特任教授和两名博士后在申请中。
